How Did This Cone Of Depression In The Groundwater Form - R = radius of well in. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? R = radius of well in metres or feet; Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web the groundwater level in the groundwater depression cone center decreased rapidly from 1990 to 1993, and. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? During the initial growth of a cone of. Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1: Web the cone of depression in the groundwater is formed when groundwater is pumped from the well faster than it can.
Little known about flow, future of aquifers News
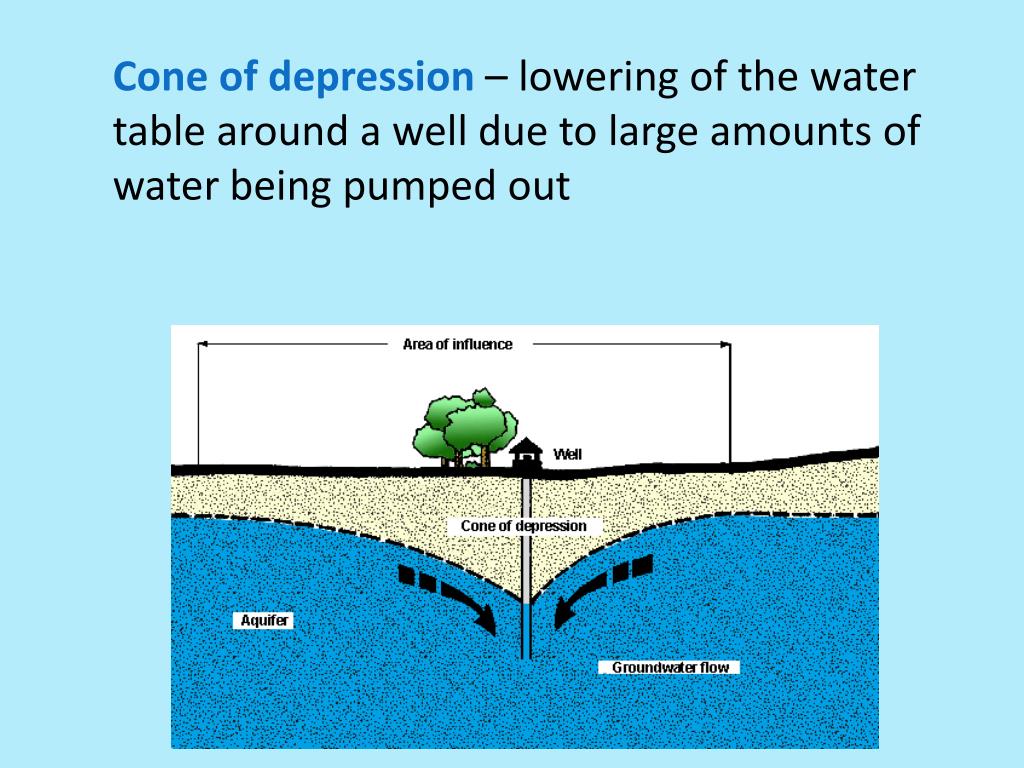
Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: Web immense cones of depression were located in beijing, langfang, baoding and xingtai, most of which were formed in the middle 1970s. Web overuse of groundwater does not have to lead to major land subsidence before it causes problems. Web the second.
PPT the Water Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2297322
Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1: Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression. How did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web salty groundwater is more dense than fresh groundwater and sits.
The cone of depression or loss of hydraulic head (From ABC's of
Web salty groundwater is more dense than fresh groundwater and sits below it in the ground: Problems with lowering of water table are common. Web this paper first develops the theory behind the calculation of the drawdown cone or cone of depression in the potentiometric surface around a potential well. An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides b. Web.
13.1 Fresh Water Supply and the Water Cycle Biology LibreTexts
R = radius of well in metres or feet; Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression. Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1: An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Web a cone of.
What Is A Cone Of Depression
Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Web salty groundwater is more dense than fresh groundwater and sits below it in the ground: Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales.
PPT ESC110 Chapter Ten Water Resources and Pollution PowerPoint
Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Problems with lowering of water table are common. During the initial growth of a cone of. An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides b.
Representation of cones of depression produced by a pumping well. The
An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression. Web overuse of groundwater does not have to lead to major land subsidence before it.
What is Cone of Depression and How is it Formed YouTube
How did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1: An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Web the groundwater level in the groundwater depression cone center decreased rapidly from 1990 to 1993, and. Web the depression of the.
PPT Groundwater Notes PowerPoint Presentation ID2343003
How did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web immense cones of depression were located in beijing, langfang, baoding and xingtai, most of which were formed in the middle 1970s. Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: Web a cone of depression is caused due to heavy.
PPT Groundwater PowerPoint Presentation ID6675315
Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web an increase in the abstraction rate of a specific well or, as is more common, an uncontrolled increase of the number of active wells in an area, could lead to. How did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides..
An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides b. Web salty groundwater is more dense than fresh groundwater and sits below it in the ground: Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web this paper first develops the theory behind the calculation of the drawdown cone or cone of depression in the potentiometric surface around a potential well. During the initial growth of a cone of. Web overuse of groundwater does not have to lead to major land subsidence before it causes problems. Web an increase in the abstraction rate of a specific well or, as is more common, an uncontrolled increase of the number of active wells in an area, could lead to. Pumping water from an aquifer lowers the water table or potentiometric surface around the well. Web immense cones of depression were located in beijing, langfang, baoding and xingtai, most of which were formed in the middle 1970s. An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Problems with lowering of water table are common. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Groundwater is pumped from the well faster than it can flow to. Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: R = radius of well in. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form? Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression. An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. R = radius of well in metres or feet; Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1:
How Did This Cone Of Depression In The Groundwater Form?
Web a cone of depression is caused due to heavy pumping in the area where the water table is located resulting in a large. Problems with lowering of water table are common. Web overuse of groundwater does not have to lead to major land subsidence before it causes problems. Web how did this cone of depression in the groundwater form?
Web Salty Groundwater Is More Dense Than Fresh Groundwater And Sits Below It In The Ground:
Web immense cones of depression were located in beijing, langfang, baoding and xingtai, most of which were formed in the middle 1970s. R = radius of well in. Web the groundwater level in the groundwater depression cone center decreased rapidly from 1990 to 1993, and. Web the depression of the piezometric surface is called the cone of depression.the characteristics of the cone of depression.
Groundwater Is Pumped From The Well Faster Than It Can Flow To.
Web an increase in the abstraction rate of a specific well or, as is more common, an uncontrolled increase of the number of active wells in an area, could lead to. R = radius of well in metres or feet; An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides. Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key:
Web This Paper First Develops The Theory Behind The Calculation Of The Drawdown Cone Or Cone Of Depression In The Potentiometric Surface Around A Potential Well.
An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides b. Web pumping has lowered the water table locally to develop a cone of depression around the well key: Web the second level uses 15 forms of land cover which can be represented on maps on scales of 1: An artesian spring flowed upward on all sides.